A Protein's Final Structure Can Include Which of the Following
Phosphoryl group on the 3-end C. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure.
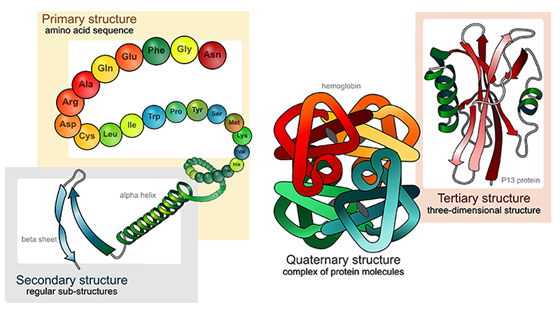
Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures
Final folded structure can reveal the steps of.

. Proteins are made of amino acids vitamins and minerals Proteins are biomolecules that are found in all living things. Primary Structure - Precise sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain held together by peptide bonds - Determines final shape - Backbone of polypeptide chain - Last to denature bc of covalent bonds Secondary Structure - Consists of regular repeated spatial patterns in different regions of a polypeptide chain. You should note that the majority of func-tional proteins exist in water and that their structures are stabilized by the forces and.
Describe the functions of protein. Factors that affect catalysts. 59 All of the following structures and proteins are directly associated with movement in cells or by cells except A cilia.
Hydroxyl group on the 5-end D. The detailed structure of any protein is complicated. The thymidine analog 3-azidothymidine AZT blocks replication of.
The attractive force involves interaction between induced dipoles formed by momentary fluctuations in the electron. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. Base on the 5end 11.
Help keep DNA compact and organized in the nucleus b. A central carbon atom is bound to an amino group carboxyl group a side chain and a hydrogen atom. Link amino acids into proteins via dehydration synthesis d.
Phosphoryl group on the 5-end B. In alpha helix protein every backbone NH group donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone CO group of the amino acid located three or four. Factors that disrupt protein structure as we saw in Section 91 Proteins include temperature and pH.
What would be the effect on the final protein product if a mutation caused the following single basepair substitution. Hydroxyl group on the 3-end E. The following points highlight the five main forces that stabilise protein structures.
Hence proteins can be distinguished based upon the amino acid composition. The secondary structure is determined by the dihedral angles of the peptide bonds the tertiary structure by the folding of proteins chains in space. Link sugar monomers into complex carbohydrates c.
A proteins final structure can include either which of the following. Final folded structure can reveal the steps of protein folding Denaturation is always irreversible Some proteins form a complete 3-D structure only when they interact with their targets Denaturation leads to bond disruption and the molecule turns into liquid. B The helices of protein are not always left handed.
The long chain exhibit specific amino acids which makes up a typical protein molecule. They are made up of long chains of amino acids. But because the final protein structure ultimately depends on this sequence this was called the.
Structure and hence the stabilityfunction of the protein. The chemical structure of a typical amino acid found in a protein. Proteins structures are made by condensation of amino acids forming peptide bonds.
Produces vital body structures providing energy providing cell structure maintaining fluid balance act as buffers contributes to immune function. The final model will be evaluated by DOPE potential. For each pair identify the strongest type of interaction between these amino acids.
-Changing environmental conditions may alter the activity of enzymes. A proteins primary structure is the unique sequence of amino acids in each polypeptide chain that makes up the protein. For simplicity a proteins structure can be depicted in several different ways each emphasizing different features of the protein.
69 Modeller can also perform additional auxiliary tasks including fold assignment calculation of phylogenetic trees and de novo modeling of loops in protein structures. Proteins possess all of the following functions EXCEPT a. Regions shaped like an α-helix or regions shaped like a β-pleated sheet but not both.
The proteins are heteropolymers. A protein has a tertiary structure formed by interactions between the side chains of the following pairs of amino acids. The executable version of the Modeller program is available for download and installation on the local computers of.
Include both an attractive and a repulsive component. E Centrosomes. To understand how a protein gets its final shape or conformation we need to understand the four levels of protein structure.
A The sequence of amino acids in a protein represents the primary structure where one amino acid is attached to the other with the peptide bond. 60 All of the following serve an important role in determining or maintaining the structure of plant cells. Which of the following are distinct from the.
5-ATGTAGTTTGGCACTTAA-3 3-TACATCAAACCGTGAATT-5 this mutation. Which of the following statements is true about proteins. Really this is just a list of which amino acids appear in which order in a polypeptide chain not really a structure.
Help proteins fold correctly 16. The primary structure or sequence of amino acids dictates the higher orders of structure including secondary a b etc tertiary often globu-lar and quaternary with multiple chains. 138139 presents four different depictions of a protein domain called SH2 which has important functions in eucaryotic cells.
Primary structure The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.

Protein Structure And Function

No comments for "A Protein's Final Structure Can Include Which of the Following"
Post a Comment